WHAT IS SUGAR DISEASE?
Diabetes
Mellitus
Is a condition when glucose is not absorbed
into the cells. Thus, it leads glucose to accumulate in blood circulation.
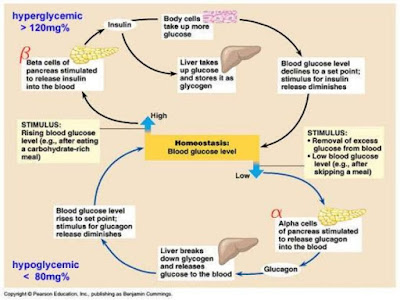
How
body react to glucose in blood ?
It
is important to know that insulin has an important role in controlling blood
glucose level. Cells need insulin to be able to absorb glucose.
Screening
for diabetes :
Normal Range :
Fasting blood glucose level : 3.5-5.5 mmol/L
2-hours post-prandial : 6.0-8.0 mmol/L
Random blood glucose level : 3.5 –
7.7mmol/L
Sign
and symptoms of diabetes mellitus:
Lethargy
Fatigue
Polyphagia
Polydipsia
Polyuria
Weight loss
Slow wound healing
Infection
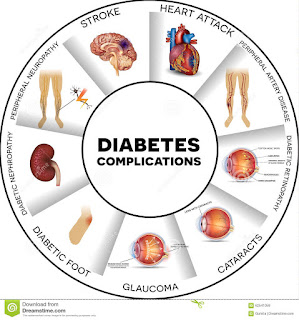
Complication
of diabetes mellitus:
Foot problems – gangrene, foot
ulcer, amputation.
Retinopathy
Nerve damage (Neuropathy)
Heart attack
Stroke
Anxiety
Type
of diabetes mellitus :
Type 1 diabetes mellitus
Ø Childhood diabetes
Ø Caused by inadequate production of insulin (Beta cell destroyed due
to autoimmune attacks)
Ø Controlled by insulin injection
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
Ø Occurs after the age of 40 and obese
Ø Pancreas retain some Beta cell function but inadequate insulin
response
Gestational diabetes
Ø Temporary condition that occur during pregnancy
Ø Increase risk of developing diabetes in mother and child.
Goals of therapy in diabetes:
HbA1c test : <7.0 %
Preprandial capillary plasma glucose :
3.9-7.2 mmol/L
Peak postprandial capillary plasma glucose
: <10mmol/L
Blood Pressure: 140/80
How
to Manage diabetes :
Glycemic control : diet/lifestyle
modification, exercise, medication
Treat associated condition such
as dyslipidemia, obese and hypertension
Screen/ manage complication of
diabetes such as retinopathy, Cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, nephropathy and foot
ulcer. Patients need to check their condition at least once a year.
Treatment
of Diabetes Mellitus
- For type 1 DM patients, they depend on exogenous insulin.
- For type 2 DM, they need to maintain glucose concentrations within normal limits to prevent long term complications. Thus, Oral hypoglycemic agents can be given. Type 2 patient also may need exogenous insulin in long term condition.
Type
of Oral Hypoglycemic Agents :
1. Insulin secretagogues : promote
insulin release from B-cells
- Sulfonylurea
- Non-sulfonylurea
- Incretins effects
- biguanide: metformin
- thiazolidinediones
Important
adverse effects and expectation:
1. Sulfonylurea : weight gain,
hyperinsulinemia, hypoglycemia.
2. Insulin sensitizer: not common
cause hypoglycemia (unless combine), drug interaction-cimetidine, furosemide,nifedipine.
3. Alpha-glucosidase inhibitor :
flatulence, diarrhea, cramping. Should not combine with metformin (decrease
bioavailability)
For more information, you can refer to the video below :
What is diabetes? Causes and Symptoms.
ATTENTION!!
If you find out that you have this symptom please refer your Doctor or Pharmacist as soon as possible. Stay with our Channel on Facebook , Instagram and our FB Page (I Am Healthy) for more info and current issue that we're focusing on from time to time. Don't forget to share your opinion and experience with us. Sharing is Caring!!.
Prevention Is Better Than Cure
REFERENCES :
1. http://www.webmd.com/diabetes/guide/types-of-diabetes-mellitus#1
2. http://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/diabetes-mellitus-an-overview
3. http://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/27/suppl_1/s5
4. Management of Diabetes Mellitus, Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia
5. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X9ivR4y03DE
6. Clinical Practice Guidelines Malaysia.
7. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2172160-overview
8. http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/722513_3




Join our Diabetic Education Club. Many activities awaiting you. Whatapp 0136283043 for more info
ReplyDelete